Distribution Panel Board Fundamentals: Know all
Electricity is supplied to your home, which is how you are able to power up your air conditioner, television, refrigerator and switch on your lights and fans. But, do you know the intricacies of the distribution of electricity? Has it ever crossed your mind how one source of electricity can provide power to so many different appliances? If you have, this article will, hopefully, satiate your curiosity.
What is an Electrical Distribution Panel board?
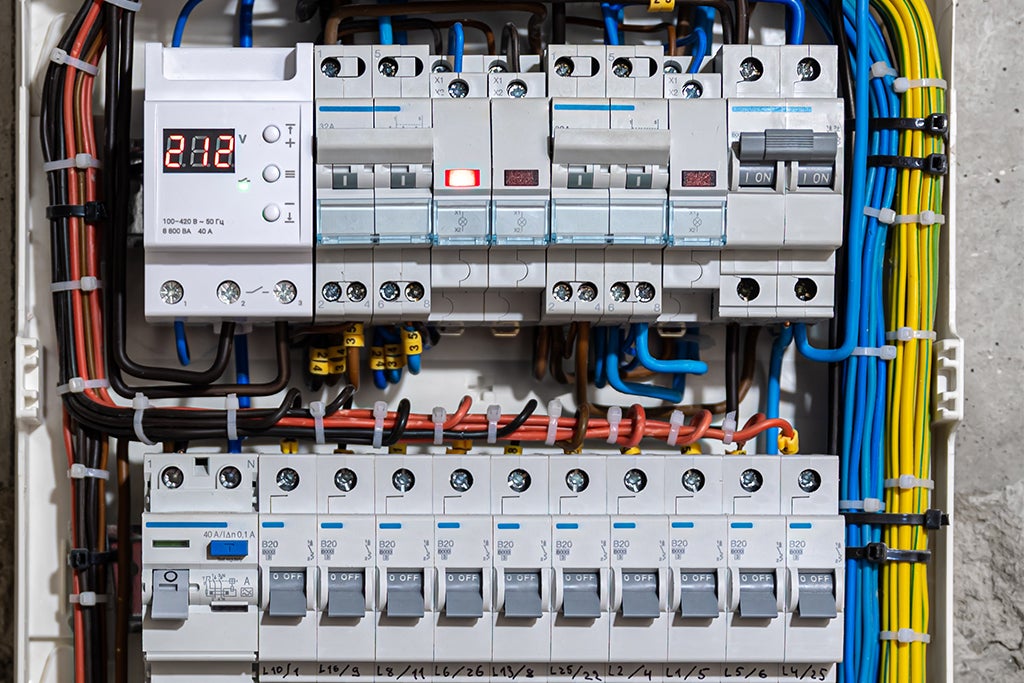
An electrical panelboard, commonly known as a distribution board or breaker panel, is a vital component in an electrical system. It serves as a centralized hub for distributing electrical power within a building or facility. The panelboard houses circuit breakers or fuses that control and protect individual circuits. Through these breakers, power is distributed to various areas of the building. Panelboards play a crucial role in electrical safety by providing a convenient point for the isolation and control of circuits, facilitating maintenance, and safeguarding against overloads and short circuits. They are essential for organizing and managing the electrical supply, ensuring efficiency and safety in the overall electrical distribution system.
Basic Functions of a Distribution Panel
A distribution panel, also known as a distribution board or breaker panel, serves as the central hub for electrical distribution within a building. Its primary functions include:
- Receives power from the main electrical supply
- Distributes electricity to various circuits throughout the building
- Contains circuit breakers or fuses to regulate the flow of electricity
- Prevents overloads and short circuits to ensure safety
- Includes switches or indicators for controlling and monitoring power distribution
- Manages electrical loads efficiently to prevent system failures
- Provides electricity to appliances, lighting, and other electrical devices
- Maintains safety standards and protects against electrical hazards
- Acts as a central hub for electrical distribution within the building
How a Distribution Panel Works
A distribution panelboard serves as a critical component in electrical systems, facilitating the safe and efficient distribution of electricity within a building or facility. Here's how distribution panelboards are typically used:
- Central Hub: The panelboard acts as a central hub where electrical power from the main supply is received and distributed to various circuits throughout the building.
- Circuit Distribution: It contains multiple circuit breakers or fuses, each dedicated to supplying electricity to specific circuits. These circuits may include lighting, outlets, appliances, HVAC systems, and more.
- Overcurrent Protection: Circuit breakers or fuses within the panelboard provide overcurrent protection. They automatically trip or blow when they detect an overload or short circuit, preventing damage to the electrical system and reducing the risk of fire.
- Load Management: Panelboards help in managing electrical loads efficiently by distributing power appropriately to different circuits. This ensures that the electrical system operates within its capacity and minimizes the chances of overload.
- Monitoring and Control: Some distribution panelboards may include switches, indicators, or meters for monitoring and controlling power distribution. This allows for easy identification of circuit status and troubleshooting of electrical issues.
Overall, distribution panelboards play a crucial role in ensuring the reliable and safe operation of electrical systems in buildings, helping to protect both property and occupants from electrical hazards.
Difference Between a Consumer Unit and a Distribution Board?
A consumer unit and a distribution board serve similar functions in electrical systems but have key differences:
Consumer Unit:
- Typically installed in residential properties
- Contains protective devices such as circuit breakers or RCDs
- Supplies electricity to final circuits within the property
- Often incorporates a main switch for isolating power to the entire property
Distribution Board:
- Commonly used in commercial or industrial settings
- Distributes power to multiple circuits or loads within a larger facility
- May contain additional components like contactors, relays, or meters
- Generally designed for higher power capacities and more complex electrical setups
Read More: Different Types of Electrical Distribution Board
What is the difference between a switchboard and a panelboard?
A switchboard and a panelboard are both components of an electrical distribution system, but they serve different functions.
- A switchboard is a larger assembly that typically handles higher voltage levels. It incorporates various devices such as switches, circuit breakers, and sometimes meters. Switchboards are commonly found in industrial settings or large commercial buildings.
- A panelboard is a smaller, more localized unit designed for lower voltage applications. It contains circuit breakers or fuses to control and protect individual circuits within a building. Panelboards are commonly used in residential, commercial, or smaller industrial settings, providing a convenient and organized way to manage electrical circuits.
Types of special-purpose panelboards
Special-purpose panelboards cater to specific applications, each designed for unique electrical needs. Some types include:
- Generator Panelboards: Facilitate the connection of generators to the electrical system, ensuring a seamless power transfer during outages.
- Fire Pump Panelboards: Dedicated to powering and controlling fire pump motors, crucial for fire suppression systems.
- Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Panelboards: Manage the distribution of power generated by solar panels, integrating renewable energy into the electrical system.
- Motor Control Centers (MCCs): Designed for controlling and distributing power to electric motors, commonly used in industrial settings.
- Instrumentation Panelboards: Tailored for housing instruments and control devices, crucial in process control and automation applications.
Each type addresses specific electrical requirements, enhancing efficiency and safety in various applications.

Comments